Monetary Policy & Monetary Policy published by the Nepal Rastra Bank. Maudrik Niti by Nepal Rastra Bank. Monetary policy is the policy formulated by the central bank to assist in the expansion of economic activities while maintaining macroeconomic stability. The macroeconomic policy introduced by the central bank of any country is called monetary policy. The objectives of monetary policy are the management of money (currency) within the country, control of inflation, balance of income and expenditure received by the country from outside, and stability of the financial sector.
Monetary policy is presented according to the conditions, needs and circumstances of the country. He has been saying that even if the rising prices are to be stopped, the interest rate should be increased and the concession given during the covid should be stopped. He said that a monetary policy will come to bring the economy to a proper place and when such a policy comes, everyone may have to tolerate something in their own place. He has repeated that it should not be considered a hardship if one has to endure something to take the economy to the right place.
Maudrik Niti NRB Monetary Policy of FY 2079/80. Some of the key points are:-
Monetary policy aims to contribute to economic growth and job creation by maintaining economic stability through money supply, credit, and interest rate management. The Rastra Bank (National Bank) has prepared to introduce a strict monetary policy. The National Bank has prepared to increase the policy rates of interest. Sources also said that the monetary policy will not allow credit flow to increase.






According to which, the risk burden has been maintained at 100 percent in share mortgage loans up to 25 lakh rupees. 150 percent risk burden will be maintained on the loan above that. Likewise, the central bank has abolished the system of holding stock transactions during mergers and acquisitions.
Now, according to the regulations made by the Securities Board, it will be decided how many days the share trading will be suspended. The capital market got relief from this arrangement.
View Full Details Page of Maudrik Niti Monetory Policy 2079 80- Read Below
What is monetary policy? Importance of Monetary Policy Maudrik Niti
Monetary policy is the policy formulated by the central bank to assist in the expansion of economic activities while maintaining macroeconomic stability. Monetary policy aims to contribute to economic growth and job creation by maintaining economic stability through money supply, credit and interest rate management.
“Monetary policy is the exercise of central bank control over money supply as an instrument for achieving the objectives of general economic policy.” Edward Shapiro
- Monetary policy is a policy made to control the money supply.
- Monetary policy is formulated by the central bank of any country.
- Nepal Rastra Bank has been formulating monetary policy in Nepal as well. When people have more money than they need, the market price goes up and monetary policy is formulated to supply money only according to the demand.
- Monetary policy is the policy of determining the level of money supply in the economy and in which areas of the economy such money should flow or be consumed.
- The monetary policy includes fiscal policy and foreign exchange policy.
- The financial policy includes policy regarding regulation of banks and financial institutions under Nepal Rastra Bank.
- As such policies have to be changed according to the demands and needs of the time, NRB brings a policy with necessary modifications every year.
Objectives & Importance of Monetary policy Maudrik Niti Importance
- maintain monetary neutrality,
- to maintain stability in exchange,
- maintaining price stability,
- to maintain full employment,
- Achieving economic growth.
- Balance of payments
Monetary policy instruments Maudrik Niti Nepal Rastra Bank
- Bank rate and refinancing rate
- Mandatory cash reserves
- Interest rate and margin rate
- Open market trading
- Debt limit and statutory liquidity
- Deposit collection
Bank & Financial Institution Circular Notice by the Nepal Rastra Bank NRB Circular
Through monetary policy, the limit of borrowing only 40 million from one bank in share mortgage loan has been abolished.
Now it is possible to take a loan up to 12 million rupees. Earlier, there was a system where you could take 40 million from one financial institution and 120 million from all.
By making some amendments, it has been arranged that 12 crores can be taken from a single bank. Similarly, some revisions have been made in the 150 percent risk weight applied to share mortgage loans.
The Rastra Bank has indicated to increase the mandatory cash balance CRR and interest rate. In addition, it is understood that Rashtra Bank is preparing to reduce the monetary facilities. The Rastra Bank has created separate indices for various goods and services sectors to measure the price increase or cost. Price increases or decreases are measured by averaging the price increases of each good and service within each bucket.
Our daily lives are directly affected by this basic concept of monetary policy. In the future, will the interest rate on loans given by commercial banks and financial institutions decrease or increase? Does the interest earned by depositing money in the bank decrease or increase?
If you are planning to build a house, buy a car or do any business by taking a loan from the bank, will your plan come true or not? Will the price of the market come under control or can it increase further?
New Government Salary Scale Sarkari Jagir Talab Scale Details

Canada Visa Apply- How To Get Canada Visa

H1B Visa America Working Visa Apply Now

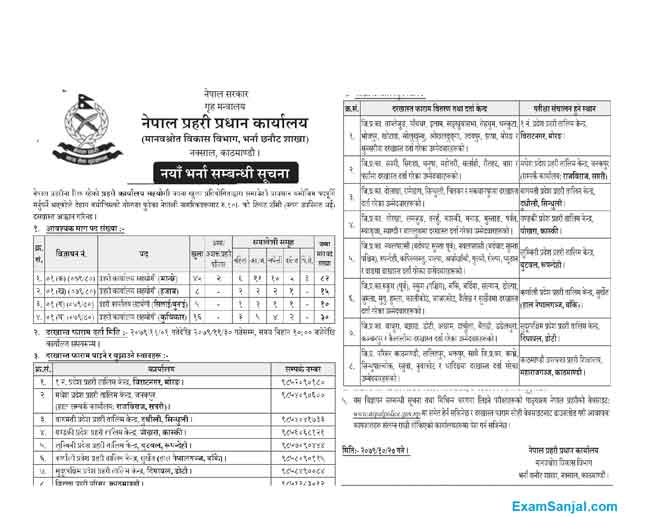
Nepal Police Job Vacancy
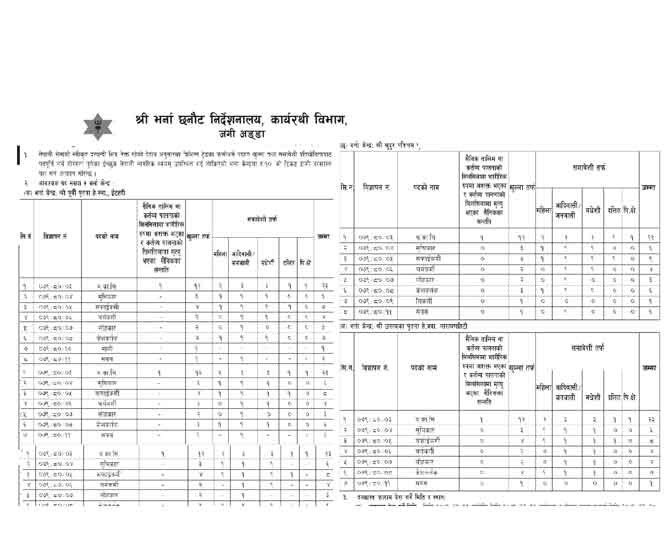
Nepal Army Nepali Sena Job Vacancy
Israel Working Visa Notice for 1000 Nepalese workers

Online Driving License Application ApplyDL.Dotm.Gov.np Apply Now


