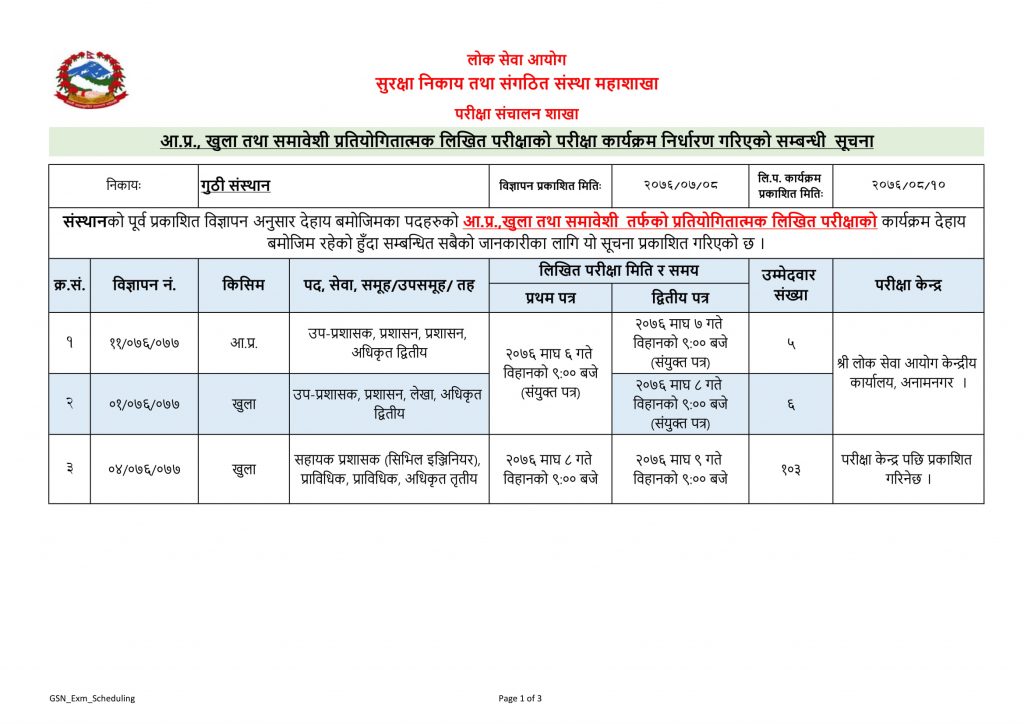
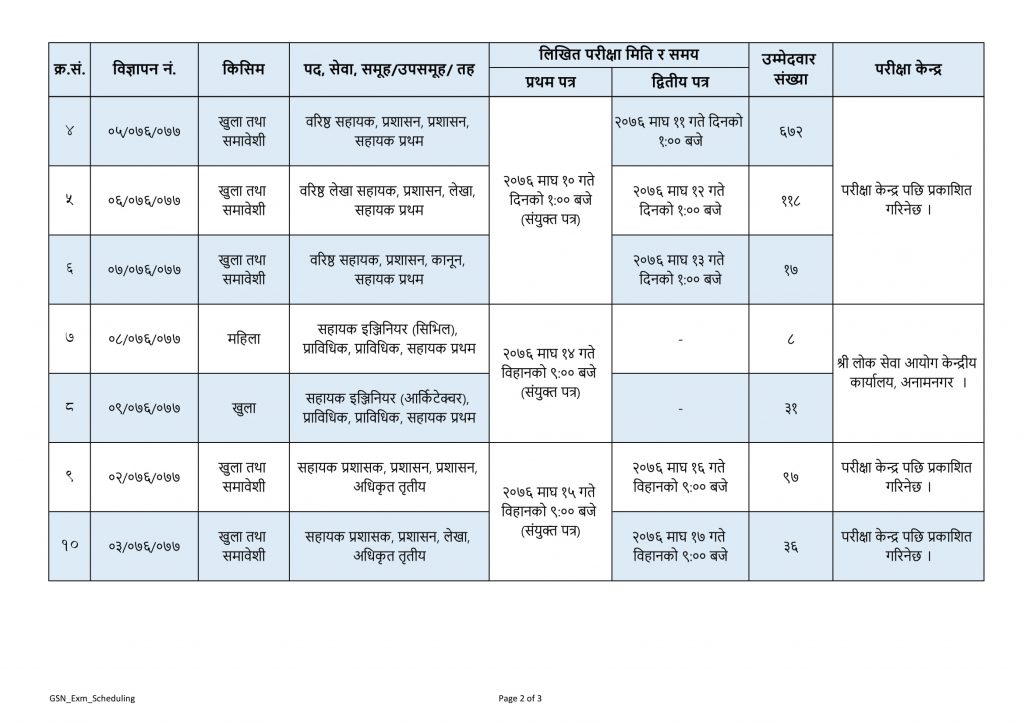
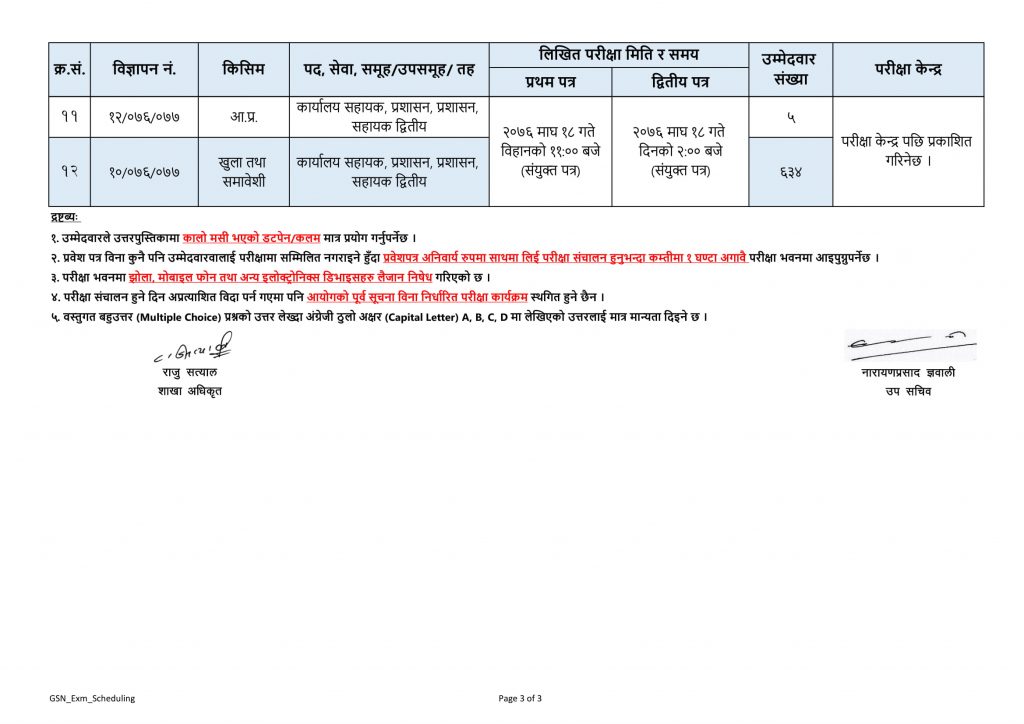
Guthi Sansthan Exam Center and Scheduled published by Lok Sewa Aayog. Guthi is traditionally a patriarchal kinship based on certain norms that are moderated by the guṭhī system. It consists of a thakali or the eldest person of the guṭhī. The consent of the thakali is essential for the formulation of most of the norms of the guṭhī. Guthi is a form of institutional landownership, the religious and charitable aspects of which have given rise to special problems and characteristics in the fields of land tenure and taxation. The Guthi is a system that has been part of the Newa social system in the Kathmandu Valley since the 5th century BC. The Guthi system is a trust, whereby land is donated to this trust. This land is then tilled upon by members of the local community and the revenue generated is not only a source of economy for the community but is also utilized to undertake various works within the community such as restoration of temples, patis (rest houses), maths (priest houses), dhunge dharas (stone water spouts) and so on. This revenue is also used to carry out various festivals, customs, rites and rituals. It was a system, therefore, that engaged the local community in terms of not only tilling the land but also engaging a group of people such as masons, shilpakars (the group of people who work with wood) and helping them to develop their skill. It also benefitted the local community economically through the revenue generated and also provided a framework within which the local community could protect their tangible and intangible culture, enabling them to protect their very identity.